Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom
Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Hydrogen Emission Spectrum, Explanation of Line Spectrum of Hydrogen, Calculation of Number of Spectral Lines & Hydrogen like Species etc.
Important Questions on Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom
According to the Bohr Theory, among the following, which transition in the hydrogen atom will give rise to the least energetic photon?
Which of the following statements do not form a part of Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom?
The energy of the second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom is . Hence, the energy of the fourth Bohr orbit would be
The energy of second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom is hence the energy of fourth Bohr orbit would be :
The Bohr orbit radius for the hydrogen atom (n = 1) is approximately The radius for the first excited state (n = 2) orbit is
The radius of hydrogen atom in the ground state is The radius of ion (Atomic number = ) in first orbit is
The spectrum of He is expected to be similar to that
In Bohr's model of hydrogen atom, the radius of the first electron orbit is . What will be the radius of the third orbit?
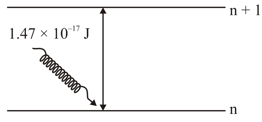
The electron in the orbit of is excited to orbit using the radiation of energy (as shown in the diagram). The value of is ___________
Given :
The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom is Its energy in the third Bohr orbit is
Given below are two statements
Statement I : According to Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom, the angular momentum of an electron in a given stationary state is quantised.
Statement II : The concept of electron in Bohr’s orbit, violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Statement-1: According to Bohr's model, angular momentum is Quantised for stationary orbits.
Statement-2: Bohr's Model doesn't follow Heisenberg's Uncertainty principle.
The ratio of radii of second and third Bohr orbits of hydrogen atoms is :
Radius of second orbit of is . Radius of fourth orbit of is . Find ?
Shortest wavelength will be for which of the following transition.
If radius of ground state hydrogen is , find out the radius of orbit of ions in .
If the kinetic energy of electron for in orbit is , then the potential energy of electron in the third excited state of is
Which of the following electronic transition occurs in H-spectrum having same wavelength as in ion spectrum when electron jumps from third excited state to first excited state.
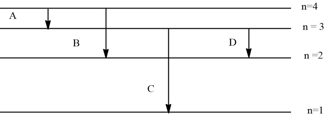
How many maximum line are observed in emission spectrum, if only two hydrogen atoms are present in the sample and electron in both atoms makes electronic transition from ?(Both electrons must follow different path)
Which electronic transition in a hydrogen atom, starting from the orbit , will produce infrared light of wave length ? (Given: )
